Conflict between the US and China export regulations on high technology
Observation of open ecosystem preoccupation strategy


There is a finding that China has a huge influence on the open source-based semiconductor intellectual property (IP) architecture 'RISC-V' camp. Chinese companies and institutions accounted for more than 50% of the members of the 'Premier Membership', which can secure seats on the RISC-V International board and technical committees. It is interpreted as a stepping stone for China to secure leadership in RISC-V, an open ecosystem, and increase its market influence despite being a subject to export restrictions on advanced technologies such as semiconductor IP from the US-China trade dispute.
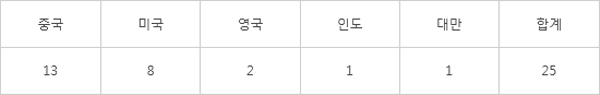
There are 13 Chinese companies and institutions based on the headquarters among the total of 25 premier members of the RISC-V alliance, 'RISC-V International’. These are more than 8 companies from the US, 2 from the UK, 1 from India, and 1 from Taiwan. RISC-V Premier members pay annual $250,000 membership fees and receive a seat on the board of directors, which is the representative of the federation, and the technical committee that leads the direction of technology development. Even thought it is fewer than 180 'strategic members', the influence they have is larger. Domestic companies such as Samsung Electronics and Semi Five are part of strategic members.
Andes Technology, Beijing Open Source Chip Research Institute (BOSC), Chengwei Capital, Xinjiang Haihe Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Computing Technology (ICT), ISCAS, Tencent, UNISOC, ZTE, and Huawei have registered as premium members in China. At the establishment of RISC-V International, US companies, such as Google, Qualcomm, Si-Five, and Western Digital was leading, and only a few Chinese companies participated; however, the number of Chinese companies are gradually increasing.
RISC-V is an open semiconductor IP architecture that has been under development since 2010, and is called 'Linux' in the semiconductor IP world. Unlike x86 led by the US’ Intel and the UK’s Arm, it is characteristic for being used without license or royalty. Many semiconductor design companies are turning their eyes to the RISC-V camp to reduce IP royalties and license costs, which are rapidly rising due to the advancement of semiconductor processes, and to increase optimization efficiency. Intel recently made an investment of $1 billion in the RISC-V camp in order to enhance the foundry service.

Semico Research, a market research firm, predicted that RISC-V-based central processing unit (CPU) IP would record an average annual growth rate of 34.9% over the next five years. This is an exponential growth compared to all semiconductor IP, which is expected to grow at around 9%. It is expected that 25 billion will be made based on RISC-V by 2027 for artificial intelligence (AI) chips.
[RISC-V International Premier Member Status by Country]
Source: RISC-V International
By Staff Reporter Dongjoon Kwon (djkwon@etnews.com)