Samsung Electronics, the Ministry of Environment, Gyeonggi Province, and public and private sectors are working together to repurpose sewage treatment water into industrial water. While solving the national issue of water scarcity by supplying the world’s biggest scale of industrial water for semiconductors from 5 sewage treatment plants, it is also able to simultaneously improve ‘environmental, social, and governance (ESG)’ management.
The Ministry of Environment revealed that the ‘Business Agreement for Sewage Treatment Water Reuse Activation’ was signed at the Samsung Electronics Hwaseong Campus on the 30th with the attendance of related government institutions, such as K-water and Korea Environment Corporation, and relevant local governing bodies in the Gyeonggi Province.
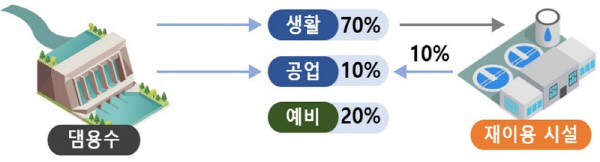
With this business agreement, 5 sewage treatment plants in Suwon, Suji, Giheung, Dongtan, and Osan will repurpose their treatment water into industrial water for semiconductor manufacturing and supply roughly 474,000 tons of treatment water daily. This is the biggest in scale globally and is equivalent to the amount of tap water used by all of the citizens in the Gwangju Metropolitan City in a day (around 484,000 tons). As this will replace dam water, it is expected to be able to secure 170 million tons of surplus water annually, which is comparable to the storage capacity of Namgang Dam (180 million tons).
The Ministry of Environment plans to use this business agreement to lay the foundation to provide reused water for semiconductor manufacturing processes, a cutting-edge industry that uses highly purified water, expand places of demand for reused treatment water, and expand the supply base.
Gyeonggi Province and local governing bodies will be able to receive supply payments from companies that use repurposed sewage water, not only helping with regional finances, but it is also expected to help invigorate the regional economy through reuse facility installment projects.
Samsung Electronics, which will be supplied with treated sewage water, is projected to be able to implement ESG management and be stably supplied with water even in times of severe droughts. In particular, it is expected that there will be advantages in reducing management risks in cases of emergencies, such as water supply restrictions.
The scale and detailed action plan of the reuse facilities will be hammered out in an upcoming commercialization stage through talks between private businesses and local governing bodies. The private and public sector plan to work together for the development of technology for highly purified water for use in semiconductor manufacturing processes.
The Ministry of Environment is planning to use the wide-area supply plan for reused sewage water as a catalyst to steadily expand the system into regions vulnerable to droughts, such as western Chungnam and southern Jeonnam. They plan to form and operate wide-area level public-private consultative bodies under the Ministry of Environment and build reuse information platforms to provide relevant information, in order to connect local governing bodies, who are the suppliers, and companies, who have the demand.
Whajin Han, the Minister of Environment, said that, “Stable supply of water is the most important essential condition for stability in citizens’ lives and company production activities,” and said that, “This business agreement will allow not only the sustainable supply of industrial water, but also securement of surplus water.” He then went on to say, “We will expand the sewage reuse project to preemptively respond to water shortages that will occur due to severe drought and climate change,” and emphasized that, “We will also do our best to develop technology for highly purified water to improve the competitiveness of the water industry.”
By Staff Reporter Junhee Lee (jhlee@etnews.com)