The Korea ? China FTA settled on the 10th is of the largest scale in terms of trade performance among Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) that have been concluded or are in the process of promotion by Korea so far. As much as so, it involves diverse interests and stakes, and thus the contents have become complicated and extensive. From the written agreement comprised of a total of 22 chapters, commodity and service market opening and product specific rule (PSR) were discussed as key issues.
◇ Commodity: Concession for aggressive profit in key industries regrettable
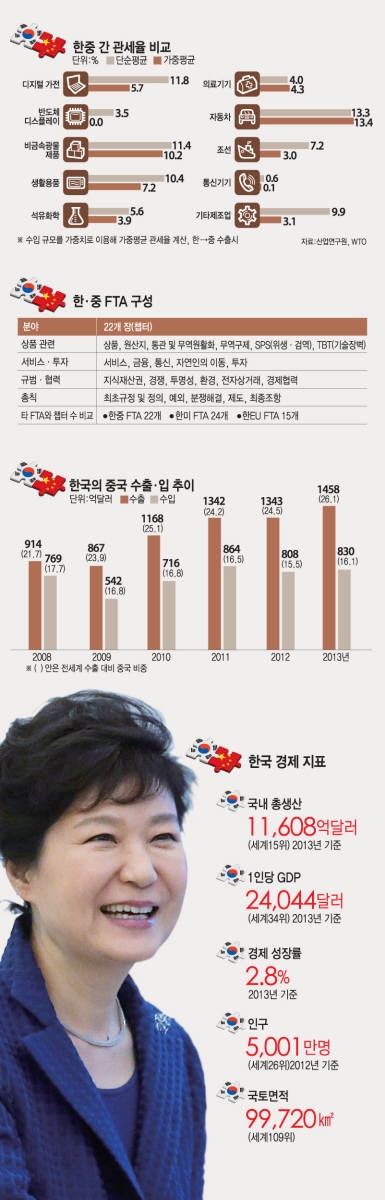
In the commodity field, which was a key issue discussed until the very end, Korea and China reached an appropriate compromise. However, the outcome of negotiation concerning industrial products was not received satisfactorily. In particular, Korea’s strategic export industries, display and automobile, were excluded from the target of aggressive profit promotion by reason that these industries have been considerably localized. Accordingly, a controversy is expected.
Korea and China agreed on lifting tariffs by 90% based on the number of items and 85% based on the import amount. China will lift tariffs by 71% based on item count and 66% based on import amount within the next ten years. As for Korea, it will lift tariffs by 79% and 77% respectively during the same period.
Korea obtained preferential tariffs for clothing, accessories and sports items as well as premium compact home appliances and medical equipments, and secured a foundation to strengthen price competitiveness of the related small companies.
On the other hand, for agricultural and fisheries products, of which Korea had been in a defensive position, Korea obtained exclusion from the concessions list at a higher rate than expected. 30% of agricultural, fisheries and livestock products, such as rice, chili pepper and garlic, based on the import amount were excluded from the concessions list. The 30% rate of exclusion from concessions list is considerably higher than of the FTAs concluded with the U.S. (0.9%) and EU (0.2%).
As a result, Korea failed to secure any particular benefits for automobile and display industries. Automobile was categorized as a highly sensitive item, and thus was excluded from the target of tariff elimination. In addition, LCD, together with refrigerator and air conditioner, was designated as an item for tariff elimination within the next ten years.
Korea’s chief FTA negotiator Woo Tae-hee from the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy explained, “Rather than pursuing profits aggressively for items of which localization has been carried out considerably, such as automobile and LCD, the concerns for key agricultural, fisheries and livestock products have been reflected as much as possible.” Although it was aimed at promoting balanced development between industrial products and agricultural industry, it was found regrettable that the value of this opportunity to expand export of the key industries was diluted.
◇ Service and Investment: From positive to negative liberalization
Considering that quite a length of time is required in the regulatory and system improvement in China, ‘positive’ type liberalization to list market opening items for both service and investment fields was stipulated. However, the two countries agreed to start a negotiation on ‘negative’ type liberalization to discuss items for market opening by principle and non-market opening within the next two years and to reach a conclusion within two years from commencement of the follow-up negotiation. Additionally, Korea has secured an opportunity for China’s service market opening, according to government sources.
In the service field, regulations restricting national treatment, number of service suppliers, business scope and the legal form of business entities were prohibited and mandatory promulgation of the service-related measures was prescribed. In terms of concession, entertainment (49% equity participation by Korean companies allowed), legal (collaboration with Chinese law firms in Shanghai Free Trade Zone), architectural and engineering (Korea’s performance recognized) and distribution (lifting of handling-prohibited items) fields were opened to Korea.
As for the investment field, it was prescribed centering on investment protection, such as in terms of national treatment and investor ? state dispute settlement. In addition, it was agreed to specify liberalization elements through follow-up negotiations.
In the communications field, a basis for entry to communications service markets of the two countries was established by alleviating regulatory barriers including mandatory provision of nondiscriminatory mutual access. China included the communications field as a separate chapter for the first time in the Korea ? China FTA.
◇ Standard and Cooperation: Will prepare a founding stone to build mutual trust
Progresses have also been made in terms of standards. The two countries guaranteed the principle of competition law enforcement, such as transparency, procedural integrity and non-discrimination, and prescribed mandatory application of competition law to public enterprises. In addition, a safeguard for domestic companies has been prepared to prevent discriminatory law enforcement upon investigation of anti-trust acts by the other country’s government. The legal ground for fair competition was further strengthened by stipulating mandatory application of obligations set forth in the competition law to China’s state-operated companies.
In relation to intellectual property rights, the countries agreed on prescription of claim for compensation by performers and music producers, stipulation of technological protection measures for copyrights and neighboring copyrights and protection of the right management information and also on extension of the broadcasting protection period from 20 to 50 years. The least measures for protection of Hallyu contents in China have also been prescribed.
In line with the digital content era, a temporary right to reproduce, which is aimed at preventing new types of intellectual property right violation, was granted and provisions on technical protection and repetitive violation prevention on the Internet have been introduced.
In the environment field, the effects of policy improvement by not only China’s central government, but also local governments are anticipated. It was agreed to apply environmental chapter of the FTA comprehensively to the local governments’ environmental laws and regulations.
e-Commerce activation between the countries is also expected. Maintenance of the customary practice to apply no tariffs to electronic transmissions as well as personal information protection and paperless trade have been reflected as non-mandatory provisions.
Lee Ho-joon | newlevel@etnews.com
[이슈분석]무난한 타결…주력산업 공세적 이익 양보 아쉬움
10일 타결된 한중 FTA는 우리나라가 지금까지 체결했거나 추진 중인 자유무역협정(FTA) 가운데 교역 실적 측면에서 최대 규모에 해당한다. 그만큼 다양한 이해관계가 엇갈리면서 타결 내용도 복잡해졌고, 광범위해졌다. 총 22개 장(챕터)로 이뤄진 협정문 가운데 상품?서비스 시장 개방과 품목별 원산지기준(PSR) 등이 핵심 쟁점으로 다뤄졌다.
◇상품 분야: 주력산업 공세적 이익 아쉬움
마지막까지 쟁점 사안이었던 상품 분야는 양국이 적절한 타협을 이뤄냈으나 공산품 측면에서는 아쉬움이 제기됐다. 특히 디스플레이?자동차 등 주력 수출산업은 현지화가 많이 진행됐다는 이유로 공세적 이익 추구 대상에서 제외돼 논란이 예상된다.
한중 양국은 품목수 기준 90%, 수입액 기준 85% 관세 철폐에 합의했다. 중국은 품목수 71%, 수입액 66%에 해당하는 품목을 10년 내 철폐하기로 했다. 한국은 품목과 수입액 기준으로 각각 79%, 77%를 같은 기간 철폐한다.
우리나라는 고급 소형 생활가전과 의료기기를 비롯해 의류?액세서리, 스포츠?레저용품 등에서 특혜 관세를 얻어내 관련 중소기업의 가격 경쟁력을 강화할 수 있는 기반을 마련했다.
반대로 수세적 입장이었던 농수산물은 예상보다 높은 양허제외율을 얻어냈다. 쌀을 비롯한 고추?마늘 등 전체 농수산축산물 수입액 기준 30%를 양허제외 품목으로 이끌었다. 30% 양허제외율은 한미(0.9%), 한EU(0.2%) 등 다른 FTA에 비해 상당히 높은 수준이었다.
이로 인해 자동차?디스플레이 등은 특별한 이익을 취하지 못했다. 자동차는 초민감 품목으로 분류돼 관세철폐 대상에서 일단 제외됐다. LCD는 냉장고?에어컨과 함께 10년 내 관세철폐 품목으로 미뤄졌다.
우태희 산업통상자원부 통상교섭실장은 “자동차?LCD처럼 현지화가 많이 이뤄진 품목에 공세적 이익을 추구하기보다는 주요 농수축산물에 대한 우려를 최대한 반영했다”고 설명했다. 공산품과 농수축산업의 균형 발전을 꾀하는 취지였지만 주력 산업의 수출 확대 기회를 희석시켰다는 점에서 아쉬움이 남았다.
◇서비스?투자: 포지티브에서 네거티브 자유화로
중국 내 법규와 제도 정비에 상당한 시일이 소요된다는 점을 감안해 서비스와 투자 모두 개방 분야를 열거하는 ‘포지티브’ 방식의 자유화를 우선 규정했다. 다만 양국은 향후 2년 내에 원칙적 개방과 미개방 분야를 다루는 ‘네거티브’ 방식의 자유화 협상을 시작하고, 후속 협상 개시 후 2년 내에 결론을 내기로 합의했다. 추가적으로 중국 서비스 시장 개방 기회를 확보했다는 게 정부 설명이다.
서비스 분야에서는 내국민 대우, 서비스 공급자 수, 사업 범위와 사업자 법적 형태 등을 제한하는 규제를 금지하고, 서비스 관련 조치 공표 의무화를 규정했다. 양허 측면에서는 △엔터테인먼트(한국기업 49% 지분 참여 허용) △법률(상하이 자유무역지대 내 중국 로펌과 합작) △건축?엔지니어링(한국 실적 인정) △유통(취급 금지품목 완화) 분야가 우리 측에 개방됐다.
투자 부문은 내국민 대우, 투자자?국가분쟁(ISD) 등 투자보호 내용 중심으로 규정됐으며 자유화요소는 후속 협상을 통해 구체화하기로 했다.
통신 분야는 비차별적 상호접속 제공 의무화 등 규제 장벽을 완화해 양국간 통신서비스 시장 진출 기반을 조성했다. 중국이 자국의 FTA에서 통신을 별도 챕터로 다룬 것은 한?중 FTA가 처음이다.
◇규범?협력 분야: 상호 신뢰 초석 마련
규범 측면에서도 진전을 이뤘다. 양측은 투명성, 절차적 공정성, 비차별 원칙 등 경쟁법 집행 원칙을 보장하고, 공기업 등에 대한 경쟁법 적용 의무 등을 규정했다. 상대국 정부의 반독점 행위 조사시 우리 기업에 대한 차별적 법 집행을 방지함으로써 우리 기업 보호장치를 마련했다. 중국 국유기업에도 경쟁법상 의무를 적용하도록 해 공정 경쟁의 법적 근거를 강화했다.
지식재산권과 관련해서는 △실연자?음반제작자의 보상청구권 규정 △저작권과 저작인접권의 기술 보호조치와 권리관리정보 보호 명문화 △방송 보호기간 20년에서 50년으로 연장 등이 합의됐다. 중국 내 한류 콘텐츠를 보호할 수 있는 최소한 장치는 규정됐다.
디지털 콘텐츠 시대 도래로 새로운 유형의 지재권 침해를 방지하는 일시적 복제권을 부여하고, 기술적 보호조치와 인터넷상 반복적 침해 방지 조항을 도입했다.
환경 분야에서는 중국 중앙정부뿐 아니라 지방정부의 정책 개선 효과가 기대된다. FTA 협정의 환경 챕터 적용 범위를 중앙정부를 넘어 지방정부의 환경법?규정?조치에도 광범위하게 적용하기로 했다.
양국간 전자상거래 활성화도 기대된다. 전자적 전송 무관세 관행 유지와 개인정보 보호, 종이없는 무역 등을 비강행 규정으로 반영했다.
이호준기자 | newlevel@etnews.com