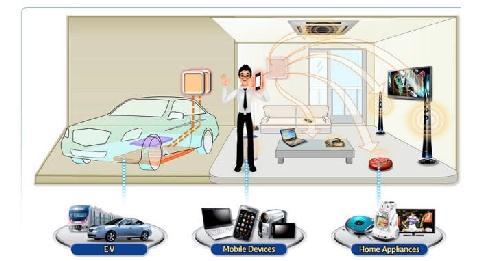
A technology for wirelessly transmitting electric power a few meters away has been developed. We will be able to do away with the cords of TVs and home appliances strewn around the house. The age of so-called ‘Cordless Home’ is dawning.
The Korea Electronics Technology Institute (KETI) announced on December 12 that it succeeded in developing the magnetic-resonance-type wireless power transmission technology. According to this technology, the transmitter creates a magnetic field and radiates it to the receiver. Energy (electric power) is delivered through this radiated magnetic field.
Its structure is similar to that of the induction range that delivers heat only to the dedicated container. The induction range delivers heat, but this technology is a high-level technology that must deliver energy without generating heat. The transmission distance of the magnetic resonance method exceeds 1m, far superior to the magnetic induction method whose transmission distance is no more than 5㎜.
The Korea Electronics Technology Institute developed a prototype and successfully demonstrated it. It can transmit 1㎾, and this energy can operate motorless TVs (power consumption less than 200~300W), vacuum cleaners (400~500W), robot vacuum cleaners (40~60W), notebooks (60W), humidifiers (40W), electric fans (30W) and smartphones (5W) at the same time. Its transmission distance is about 1.2m, and if the hub, called a ‘relay,’ is installed, the distance can be increased. For this demonstration, two relays were used and electric power was transmitted as far as 4m. Theoretically speaking, an unlimited number of relays can be installed.
It will be possible to commercialize this technology for products consuming little energy, such as cell phones, as early as the end of next year. Household appliances seem likely to be commercialized in 2016. To prevent the controversy over health risks, the Korea Electronics Technology Institute is planning to use the avoidance technology. KETI said, “As there is a controversy over health risks, we are thinking of blocking electric power if a person approaches or making electricity flow on the wall.”
The Korea Electronics Technology Institute spent more than 5 years in developing this technology. It holds 88 patents at home and abroad. KETI said that no similar technology has been confirmed overseas yet.
As this technology made the landline phone disappear, the cordless home will become possible. Many application products, such as robot vacuum cleaners that don’t need to be recharged, are forecast to appear.
“The last thing to lose before the opening of the cordless age is the ‘electric wire,’” said Lim Seung-ok, head of the Communication Network Research Center of KETI. “As this technology can be used in various areas, such as smart devices, home appliances and automobiles, it has unlimited growth potential.”
※ Glossary: Magnetic resonance method ? This wireless power transmission technique was widely known by a paper published in 2007 by Prof. Marin Soljacic of MIT. Unlike the magnetic induction method that was invented 100 years ago, it has no restriction in distance. So it has been attracting popular attention as the next-generation wireless power transmission technique. According to the magnetic induction method, the transmitter creates a magnetic field and delivers electricity to the receiver 5㎜ away. According to the magnetic resonance method, the transmitter creates a magnetic field vibrating at the resonance frequency, radiates it to the receiver designed with the same resonance frequency and transmits energy.
Kim Joon-bae | joon@etnews.com
전선없는 가정 시대 이끌 핵심기술 나왔다
몇 미터(m) 떨어진 곳까지 무선으로 전력을 전송할 수 있는 기술이 개발됐다. 집 안 구석에 어지럽게 널린 TV?가전제품의 전선을 없앨 수 있게 된다. 이른바 `코드리스 홈(Codeless Home)` 시대의 개막이다.
전자부품연구원은 자기공진방식의 무선전력전송 기술 개발에 성공했다고 12일 밝혔다. 무선전력전송기술은 송신부에서 자기장을 생성해 수신부에 복사하는 방식으로 에너지(전력)는 복사되는 자기장을 통해 전달한다.
전용용기에만 열을 전달해 데우는 인덕션 레인지와 유사한 구조다. 인덕션 레인지는 열을 전하지만 이번에 개발한 기술은 열을 내지 않으면서 에너지를 전달해야 하는 고단위 기술이다. 자기공진방식은 전달거리가 1m 이상으로 5㎜에 불과한 자기유도방식과 비교해 월등히 뛰어나다.
전자부품연구원은 프로토타입을 개발해 시연에 성공했다. 1㎾를 전송하며 이 에너지는 모터를 사용하지 않는 TV(200~300W?이하 전력소비량) 청소기(400~500W) 로봇청소기(40~60W) 노트북(60W) 가습기(40W) 선풍기(30W) 스마트폰(5W) 등을 동시에 가동할 수 있다. 전송거리는 1.2m정도며 `릴레이`라는 허브를 놓으면 거리를 늘릴 수 있다. 이번 시연에서는 두 개의 릴레이로 4m까지 전송에 성공했다. 이론적으로 릴레이는 무한대로 놓을 수 있다.
상용시점은 휴대폰과 같이 에너지가 적은 제품은 이르면 내년 말에 가능하다. 가전제품은 2016년에 상용이 가능할 것으로 본다. 전자부품연구원은 인체 유해성 논란을 막기 위해 회피기술을 탑재할 계획이다. 연구원 측은 “유해성 논란이 일 수 있는 만큼 사람이 접근하면 전력을 차단하거나 벽을 타고 전력을 흐르게 하는 등의 방식을 고민하고 있다”고 말했다.
전자부품연구원은 이 기술 개발에 5년여의 시간을 투입했다. 국내외 등록 특허가 88개에 달한다. 연구원 측은 해외에서 확인된 유사 기술은 없다고 전했다.
기술이 구현되면 유선전화기가 사라졌듯이 집 안에 전선이 없는 코드리스 홈이 가능해진다. 충전이 불필요한 로봇청소기 등 다양한 응용 제품도 등장할 전망이다.
임승옥 전자부품연구원 통신네트워크연구센터장은 “코드리스 시대를 여는 마지막 선이 `전선`”이라며 “이 기술은 스마트기기뿐만 아니라 가전제품?자동차 등 다양한 분야에서 활용이 가능해 앞으로 성장 잠재력이 무궁무진하다”고 강조했다.
※용어설명:자기공진방식-2007년 미국 MIT대학의 마틴 솔라리치 교수 논문 발표로 알려진 무선전력전송기법이다. 100년 전에 구체화된 자기유도방식과 달리 거리 제약이 없어, 차세대 무선전력전송기법으로 관심을 받아왔다. 자기유도방식은 송신부에서 자기장을 발생해 5㎜ 정도 떨어진 수신부에 전기를 유도하는 전자기 유도 원리다. 자기공명방식은 공진 주파수로 진동하는 자기장을 생성해 동일한 공진 주파수로 설계된 수신부에 복사하며 에너지를 전달한다.
김준배기자 | joon@etnews.com