Samsung Display has decided not to use BCS (Black Column Space), which was newly introduced to LCD production process, and return to using previous method because its profitability received significant amount of damage as yields rapidly dropped due to introduction of a new process in first quarter. Samsung Display is planning to apply BCS again next year after increasing level of perfection of BCS.
According to an industry on the 25th, Samsung Display has decided to remove BCS that it newly introduced to its production corporation in Suzhou, China end of last year. By returning to previous method of production technology, Samsung Display’s plan on introducing a new process has gone back to a starting point.
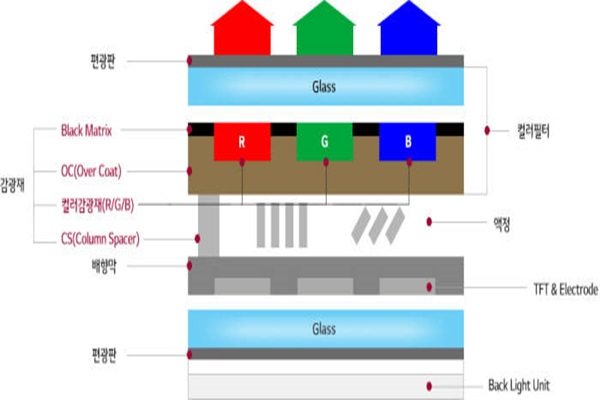
BCS is a new material that combines a black matrix that fills gaps between pixels and a column spacer that maintains distance between upper and lower glass substrates into one.
Samsung Display introduced BCS after introducing COT or COA (Color Filter on TFT Array) process that puts a color filter on top of lower TFT (Thin Film Transistor) right away instead of exposing upper layer.
Although upper and lower layers need to go through exposure process during COT process, number of photomasks can be reduced since only bottom layer is exposed. Because penetration ratio of pixel increases as distance between a color filter and a glass substrate decreases, consumption of electricity for panels can be reduced.
Although level of difficulty of this technology is high, time and cost for production can be reduced since this technology reduces material cost and number of processes used. Overall, it can bring positive effects in reducing production cost of LCDs.

Although Samsung Display introduced COT process and new BCS process to its production lines, it had had significant amount of difficulty in securing stable yields. Even though it tried hard during first quarter, it has eventually decided to mass-produce LCD panels by using previous method.
Because Samsung Display made operating loss from its LCD business in first quarter, it made loss from its overall performance.
Stock firms are estimating that Samsung Display made between $347 million and $521 million (400 billion KRW and 600 billion KRW) in operating loss from its LCD business in first quarter. Industries think that this decision made by Samsung Display is unusual because sudden variables can happen at lines for mass-production unlike lines for testing.
“Because there are problems regarding yields if new display and semiconductor technologies are introduced, businesses verify display and semiconductor technologies for about a year and a year and half and three years respectively and minimize early problems.” said one representative for an industry. “It is unusual to see a business take out a technology that is already decided to be used for mass-production from production lines.”
It is heard that Samsung Display is going to solve problems regarding COT process and BSC technology by end of this year and is planning to apply them again to its mass-production lines.
Many LCD panel manufacturers such as LG Display, Taiwan’s AUO and others already introduced COT process and are using them.
As Samsung Display is putting off introduction of a new process, there is a higher chance that its LCD business will recover in second quarter. Although it still needs to solve problems such as change in thickness of glass substrates for LCD TVs, oversupply in markets and others, it is expected that part of its performance, which temporarily took a nose dive, might recover if yields of LCDs are increased. Regarding a question about this case of changing its decision not to use a new process, Samsung Display answered by saying that it cannot give any detailed information about it.
Staff Reporter Bae, Okjin | withok@etnews.com