
Samsung Electro-Mechanics has developed a multilayer ceramic capacitor (MLCC) used in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). Samsung Electro-Mechanics, the largest in Korea and second in the world, is concentrating its efforts on the automotive electronics market. ADAS helps drivers with convenience and safe driving, such as Lane Departure Warning System(LKAS), Smart Cruise Control (SCC), and Surround View Monitor (SVM).
On the 12th, Samsung Electro-Mechanics announced that it has developed two types of MLCCs for ADAS. The new product is small with a capacity of 100 nano farads (nF) in the 0603 (0.6mm in width and 0.3mm in length) size and another one with 47 microfarads (uF) ultra-high capacity in 3216 size.
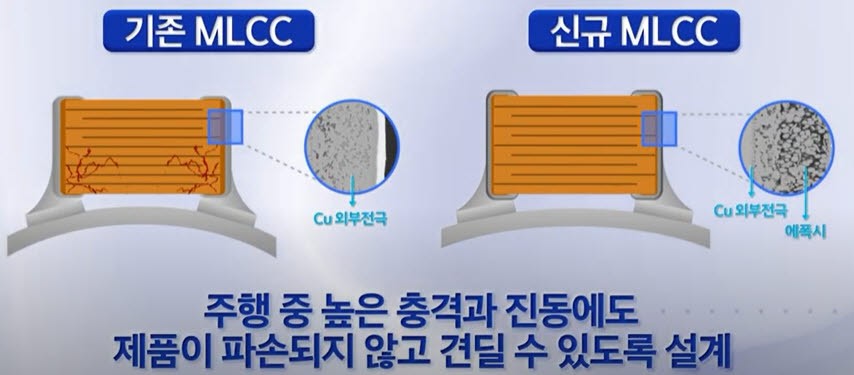
The feature of 0603 MLCC is it has reduced the area by 64% from the previous 1005 product, while the capacitance is 100nF, the same as that of the 1005 product. Mounted on the signal end of the 'automobile electronic control unit' (ECU), it helps deliver accurate signals by removing surrounding signal noise (noise). To prevent damage to the MLCC from shocks and vibrations transmitted during driving, the flexural strength has also been strengthened more than twice the standard. 0603 MLCC satisfies AEC-Q200, the automotive electronic component reliability test standard. The 3216 MLCC is characterized by more than double the capacity (47uF) from the existing product. Thanks to greater capacity, MLCC can stably supply power to the semiconductors in a vehicle. These days, in-vehicle semiconductors are being upgraded to process more data quickly as ADAS functions are advanced. High-performance semiconductors require high power consumption, so high-capacity MLCC that can store a huge amount of energy and supply it quickly is important. Samsung explained that it achieved the industry's highest capacity among same size products by miniaturizing dielectric ceramic powder, the core material of MLCC, to a nano level and applying an ultra-precise lamination method. It also increased the rated voltage (the highest voltage that can be withstood without being damaged by voltage) by 1.5 times (4V → 6.3V) from the existing product to strengthen durability.
Samsung Electro-Mechanics completed the construction of an MLCC plant for electric equipment in Tianjin, China in the 2Q of last year. It is the expansion of an electric MLCC production base following Busan to accelerate the expansion of the electric MLCC business. This is because the MLCC market for electric vehicles is growing with the evolution of automobiles such as electric and autonomous vehicles. As the number of ECU installations increases due to the increase of convenience functions and the number of ADAS modules grows due to stronger autonomous driving functions, the MLCC market for automotive applications is expected to increase at a CAGR of 20% until 2025.
Samsung Electro-Mechanics started mass-producing MLCCs for electric vehicles in 2016. Murata and TDK are leaders in this field. Although they are the world's second largest MLCC company, they are latecomers in MLCC for automotive applications. But since the market is growing so fast that 10,000 MLCCs are installed per vehicle, Samsung Electro-Mechanics has set a goal of becoming second in the industry by 2022.
Doo-young Kim, head of Samsung Electro-Mechanics’ Component Business division (Vice President), said, “Demand for compact, high-performance, and high-reliability MLCCs is significantly increasing due to the advancement of vehicles. We will fort if your tech competitiveness by developing and manufacturing core raw materials for MLCCs ourselves and expand our market share in MLCCs for automotive use by internalizing facilities and expanding production capacity.”

Gun-il Yoon, Staff Reporter benyun@etnews.com