Japan, which is a powerhouse in materials and parts, is damaging global market ecosystem through collusion.
Many incidences of Japan impeding fair competitions between businesses by supplying materials and parts that are used for cars, Smartphones, and electronic devices to global markets and causing collusion have been exposed. Out of entire international collusions exposed by Fair Trade Commission (FTC) in the past 17 years, 77% of them involved Japanese businesses. However, Japanese businesses were able to avoid punishments in some cases by abusing leniency system.
South Korea, which is highly dependent on foreign trades, can be significantly damaged from international collusion. As a result, many point towards the need for strict observation and punishment by South Korean Government.
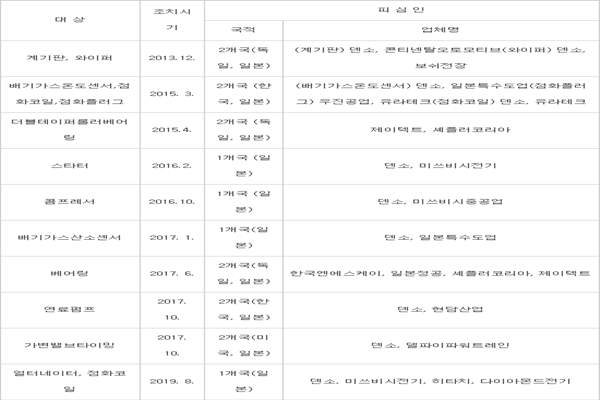
According to South Korean Government, FTC recently exposed and imposed sanctions on Mitsubishi Electric, Hitachi, DENSO, and Diamond Electric for collusion and finalized ‘global collusion of automotive parts’ incident that had lasted seven years.
This incident had also taken place in the U.S. and EU (European Union). Many countries have carried out their own respective investigations and sanctions. South Korea started investigating in 2013 and it imposed sanctions on ten cases. About 13 automotive parts were involved in collusion within South Korean Market. South Korean Government levied $157 million (190 billion KRW) in fines until now.
Japanese businesses lie at the center of the incident. All ten cases exposed by FTC involve Japanese businesses. DENSO especially is involved in eight cases and it had played a major role in this incident.
“All ten cases exposed by FTC come down to single root.” said a representative for the industry. “Some Japanese businesses were able to avoid fines and lawsuits by abusing our leniency system.”

Price-fixing by Japanese businesses is not limited to automotive parts. In 2018, FTC exposed nine Japanese businesses that were involved in price-fixing within South Korean market for condenser that is used for Smartphones and others. In South Korea alone, they were involved in price-fixing for 14 years and they had also affected the U.S., EU, Taiwan, and Singapore.
According to the analysis done by The Electronic Times on fair trade white paper, FTC has so far processed 26 major price-fixing cases after it imposed sanctions for the first time in 2002. It was confirmed that 20 cases (77%) involve Japanese businesses. Japanese businesses were mostly involved in materials and parts such as graphite electrode bar, Braun tube glass, automotive parts, and condenser.
‘Price-fixing’ lies on the other side of Japan that is known as a powerhouse in materials and parts. Reason why so many Japanese businesses are involved in price-fixing is because there is an unusual corporate culture called ‘respect to vested rights’ within Japanese society. It is heard that a Japanese business that was recently exposed by FTC expressed implicitly that it respects vested rights of its current suppliers and that it will not compete with them.
Industries point out that price-fixing must be eradicated through strict sanctions as it disrupts global market ecosystem. “Because our country highly depends on foreign trades and imports major raw materials, we can be hugely affected through international price-fixing.” said FTC.
“International price-fixing has negative impact on our economy.” said a representative for FTC. “We are going to tighten our monitoring in other areas besides automotive parts and we are going to impose strict sanctions once we expose price-fixing.”
Staff Reporter Yoo, Seonil | ysi@etnews.com